Motors and fans are generally utilised as a part of different divisions where mechanical energy is required. It is an electromechanical device which converts over electrical energy into rotary mechanical energy. This yield is then additionally changed over to give the required final use-energy. The two principle segments of engine are the stator (stationary component) and the rotor (rotating component). Motors are the most important driving components of industrial and consumer products. Motor system applications bring the convenience of automation to humanity.
Energy-efficient ceiling fans. Ceiling fans are large fans that are attach to the ceiling, and work by circulating the air in the room, pushing air down. This creates a “wind chill” effect that provides relief through evaporative cooling. The fan converts electric energy into kinetic energy that does work, and it converts some electric energy into heat. This central location in the room give the fan a better vantage point from which to circulate air. Additionally, the blades for a ceiling fan are much longer than a standing fan’s blades which helps ceiling fans to move air more effectively than standing fans do.
Unlike air-conditioning, a ceiling fan doesn’t actually make the air in a room or space cooler. Instead, the fan cools the occupants in it. The breeze from a properly sized and placed ceiling fan cools occupants by disrupting the stagnant layer of air that surrounds the body, preventing heat loss.
Types of Energy-Efficient Fans
- Ceiling Fan
- Whole-House Fans
- Window Fan
- Tower Fan
- Smart Fan
Advantages
They are easily installed. They provide lighting in addition to heat relief (or can be retrofitted with lights). They consume less energy
Working Cycles of fans :-
Fans Calculation :-
Design in brief

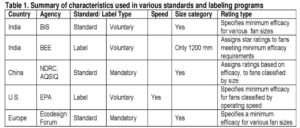
Global Standard
Material used
Industrial or commercial ceiling fans typically use three or four blades, typically made of either steel or aluminum, and operate with a high-speed motor. These energy efficient ceiling fans are designed to push massive amounts of air across large, wide open spaces.
Precautions applicable
For maximum efficiency, the fan should be set around eight to nine feet above the floor. Fans with low profiles are available for ceilings that are lower than eight feet. As well, fans should be at least 18 inches away from walls and doors to prevent blades from hitting.
End point
Still many experiments are going on for the latest technology of the energy efficient fans. Many countries doing trial and error method to do for the utilization of its best and to know the upcoming result by doing prototype experiments
This article is authored by: Talib Haque Khan, B.E (Mech)
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.